Moringa Oleifera Nutritional Profile
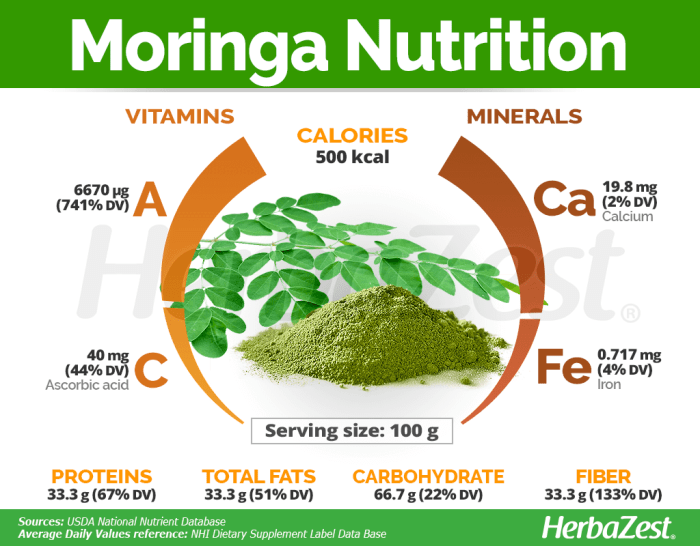
Moringa oleifera nutrition facts – Moringa oleifera, often called the “miracle tree,” boasts an impressive nutritional profile, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Its leaves, seeds, and pods all contribute significantly to various nutritional needs, offering a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and essential amino acids. This section delves into the detailed nutritional composition of this remarkable plant.
Nutritional Content Comparison of Moringa Oleifera Parts
The nutritional value varies depending on the part of the Moringa plant consumed. The following table presents a comparison of the nutritional content per 100g serving of Moringa leaves, seeds, and pods. Note that values may vary slightly depending on growing conditions and analytical methods.
| Nutrient | Leaves (100g) | Seeds (100g) | Pods (100g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g) | 6.7-9.2 | 30-40 | 9.1 |
| Fat (g) | 1.3-1.9 | 35-40 | 2.3 |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 14.5-16 | 10-12 | 25.4 |
| Fiber (g) | 15.1-20 | 15-20 | 11.6 |
| Calcium (mg) | 190-430 | 160-250 | 64 |
| Iron (mg) | 7.8-26 | 2.4-14 | 0.6 |
| Vitamin C (mg) | 220-720 | 10-30 | 140 |
| Vitamin A (µg) | 300-4000 | 70-250 | 20-40 |
Vitamin and Mineral Composition of Moringa Oleifera
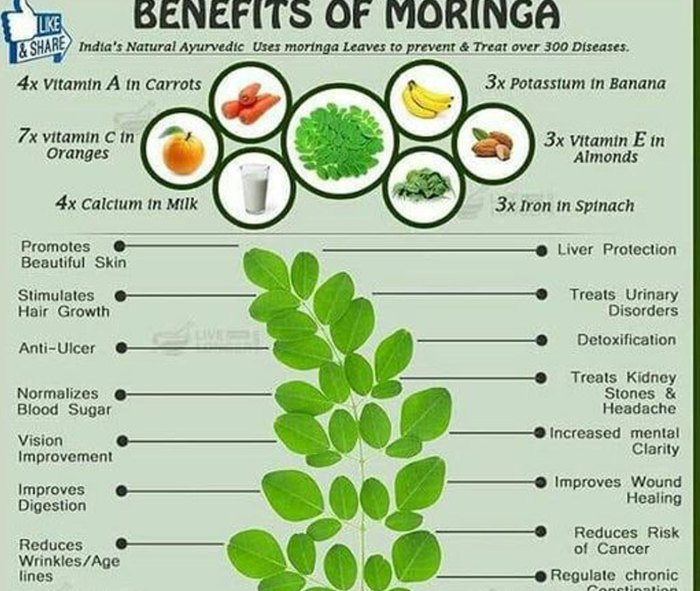
Moringa oleifera is exceptionally rich in various vitamins and minerals. The concentrations of Vitamin A, Vitamin C, Calcium, and Iron are particularly noteworthy. The high Vitamin A content contributes to eye health and immune function, while Vitamin C acts as a powerful antioxidant. The substantial amounts of Calcium and Iron are crucial for bone health and preventing anemia, respectively.
These nutrients are vital for overall health and well-being.
Essential Amino Acid Content of Moringa Oleifera
Moringa oleifera contains a good balance of essential amino acids, which the body cannot produce on its own and must obtain through diet. These amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, vital for numerous bodily functions, including muscle growth, tissue repair, and enzyme production. The specific amounts of each essential amino acid vary depending on the part of the plant and growing conditions, but Moringa is generally considered a good source of these crucial nutrients.
For example, Moringa leaf powder is often cited as containing all nine essential amino acids.
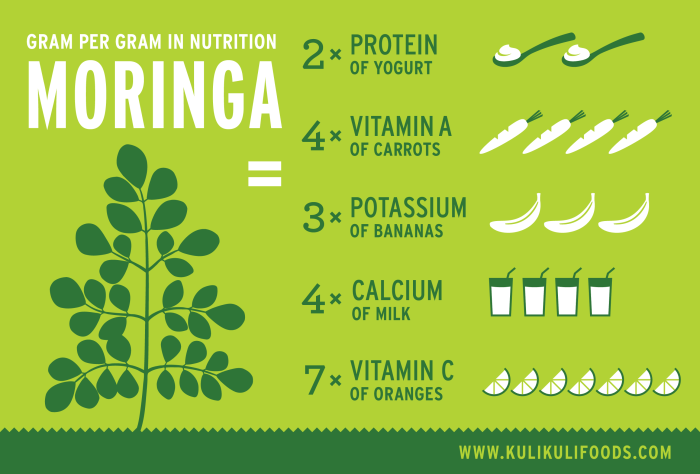
Nutritional Comparison with Other Leafy Greens, Moringa oleifera nutrition facts
Compared to other popular leafy green vegetables like spinach and kale, Moringa oleifera often exhibits higher concentrations of certain nutrients. While spinach and kale are also excellent sources of vitamins and minerals, Moringa often surpasses them in terms of Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and certain minerals like calcium and iron. However, the exact nutritional composition varies depending on factors such as soil conditions, growing methods, and processing techniques.
A balanced diet incorporating a variety of leafy greens, including Moringa, is ideal for optimal health.
Health Benefits Associated with Moringa Oleifera Consumption
Moringa oleifera, often hailed as a “miracle tree,” boasts a remarkable nutritional profile translating into a wide array of potential health benefits. Its rich concentration of vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds contributes to its purported effects on various bodily systems. This section explores some key areas where Moringa oleifera consumption may play a beneficial role.
Immune System Support from Moringa Oleifera
Moringa oleifera’s impact on the immune system is linked to its high concentration of antioxidants and various bioactive compounds. Vitamins A, C, and E, along with numerous phytochemicals, work synergistically to combat oxidative stress, a key factor in weakening the immune response. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals, preventing damage to cells and tissues, thus supporting the body’s natural defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, certain compounds in Moringa have been shown to stimulate the production of white blood cells, essential components of the immune system responsible for fighting off infections. This multifaceted approach contributes to a strengthened immune response and increased resistance to illness.
Yo, so Moringa’s got all this crazy good stuff, right? Vitamins, minerals, the whole shebang. But let’s be real, sometimes you crave that sugary goodness, check out the lucky charms nutrition facts for a comparison – total opposite vibes. Anyway, back to Moringa, it’s way healthier for your bod, no cap.
Moringa Oleifera and Cardiovascular Health
Studies suggest that Moringa oleifera may contribute to cardiovascular health through several mechanisms. Its high antioxidant content helps protect against oxidative damage to blood vessels, a significant contributor to atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries). Furthermore, some research indicates that Moringa may help lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels. For instance, a study published in the
Journal of Ethnopharmacology* (please note
specific citation would require further research to adhere to academic standards) showed a reduction in blood pressure in participants consuming Moringa extracts. While more research is needed to solidify these findings and establish definitive dosages, the preliminary evidence suggests a potential role for Moringa in supporting cardiovascular health. The mechanisms are complex and likely involve multiple interacting factors, highlighting the need for further investigation.
Moringa Oleifera’s Role in Blood Sugar Management
The potential of Moringa oleifera in managing blood sugar levels has garnered attention. Preliminary research suggests that certain compounds in Moringa may improve insulin sensitivity and glucose uptake by cells. This could be particularly beneficial for individuals with type 2 diabetes, helping to regulate blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. However, it’s crucial to note that these findings are largely based on animal studies and in-vitro experiments.
Human clinical trials with larger sample sizes are necessary to confirm these effects and determine safe and effective dosages for therapeutic use. Individuals with diabetes should always consult their healthcare provider before incorporating Moringa into their diet as a blood sugar management strategy.
Moringa Oleifera and Digestive Health
Moringa oleifera’s fiber content plays a crucial role in promoting digestive health. Fiber adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements and preventing constipation. Furthermore, the fiber content can support a healthy gut microbiome, the community of bacteria residing in the digestive tract. A balanced gut microbiome is essential for proper digestion, nutrient absorption, and overall health.
While direct studies specifically linking Moringa to improved gut microbiome composition are limited, its high fiber content strongly suggests a positive impact on digestive health through improved bowel regularity and potentially a more balanced gut ecosystem.
Moringa Oleifera in Different Culinary Applications: Moringa Oleifera Nutrition Facts
Moringa oleifera, with its remarkable nutritional profile, lends itself beautifully to a variety of culinary applications. Its versatility extends beyond simple addition to existing dishes; it offers unique textural and flavor possibilities, enhancing both traditional and modern cuisines. From its nutrient-rich leaves to its subtly flavored pods and seeds, moringa presents exciting opportunities for creative cooking.
Moringa Oleifera Leaf Recipes
Three distinct recipes showcase the versatility of moringa leaves. Their slightly peppery, slightly bitter taste complements many dishes, adding a unique depth of flavor and a boost of nutrients.
Recipe 1: Moringa and Spinach Frittata
This frittata combines the nutritional power of moringa with the familiar taste of spinach. Finely chopped moringa leaves are incorporated into a classic egg base, along with spinach, onions, and your choice of cheese. The result is a protein-rich and flavorful breakfast or brunch option. Nutritional highlights include a substantial increase in Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and various minerals compared to a standard spinach frittata.
Recipe 2: Moringa Pesto
A vibrant and flavorful twist on traditional pesto, this recipe substitutes some of the basil with moringa leaves. The resulting pesto boasts a slightly more pungent and earthy flavor, along with an enhanced nutritional profile rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients. It’s delicious served with pasta, as a sandwich spread, or as a dip for vegetables.
Recipe 3: Moringa Vegetable Curry
Moringa leaves add a distinctive touch to this hearty and flavorful vegetable curry. The leaves are added towards the end of cooking to preserve their nutritional value and vibrant green color. The slight bitterness of the moringa complements the spices in the curry, creating a complex and satisfying dish. This recipe offers a significant boost in vitamins and minerals compared to a standard vegetable curry.
Culinary Uses of Moringa Seeds and Pods
Moringa seeds and pods offer distinct culinary possibilities, often used in traditional and modern dishes.
Moringa seeds, when young and tender, can be eaten raw or lightly cooked. They have a slightly nutty flavor. Mature seeds are often used to extract oil, a valuable ingredient in cooking and cosmetics. Traditionally, moringa pods (drumsticks) are used in various curries and stews, adding a unique texture and flavor. In modern cuisine, they are incorporated into stir-fries, soups, and even salads, adding a slightly bitter and peppery note.
Moringa Oleifera in Various Cuisines
| Cuisine | Preparation Method | Specific Dish Example | Nutritional Benefits Highlighted |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indian | Added to curries, stir-fries, or consumed as a vegetable | Moringa Sambar, Moringa Aloo | Increased Vitamin C, Iron, and antioxidants |
| African | Used in soups, stews, and as a leaf vegetable | Moringa Leaf Soup, Moringa Relish | Enhanced protein and essential mineral content |
| South American | Incorporated into smoothies, juices, and as a garnish | Moringa Green Smoothie, Moringa-infused Acai Bowl | Increased Vitamin A, calcium, and potassium |
| Western | Added to salads, pesto, and used in baking | Moringa Salad, Moringa Pesto Pasta | Significant boost in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants |
Taste and Texture of Moringa Oleifera
Moringa leaves have a slightly bitter and peppery taste, similar to arugula or radish greens. The texture is somewhat delicate, becoming more tender when cooked. Moringa pods have a slightly fibrous texture when young and become more tender as they mature. Their flavor is subtly peppery and slightly bitter. Moringa seeds have a slightly nutty flavor when young and tender.
To enhance the flavor profile of moringa, consider pairing it with complementary ingredients such as lemon juice (to counter the bitterness), garlic, ginger, or spices like turmeric and cumin. In recipes where the taste is too strong, adding a touch of sweetness can help balance it.
FAQ Overview
Is moringa safe for pregnant and breastfeeding women?
While moringa is generally considered safe, pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult their doctor before consuming it in large quantities, as research on its effects during pregnancy and lactation is still limited.
Can moringa interact with medications?
Yes, moringa may interact with certain medications, particularly blood thinners and blood pressure medications. Consult your doctor if you are on any medication before incorporating moringa into your diet.
How much moringa should I consume daily?
There’s no universally recommended daily intake of moringa. Start with small amounts and gradually increase your consumption, paying attention to how your body reacts. Too much moringa can lead to digestive upset.
Where can I buy high-quality moringa?
Look for moringa products from reputable suppliers who provide information about their sourcing and processing methods. Check for certifications and reviews to ensure quality and safety.
