Calorie Content and Serving Sizes: Chocolate Chip Cookie Nutrition Facts
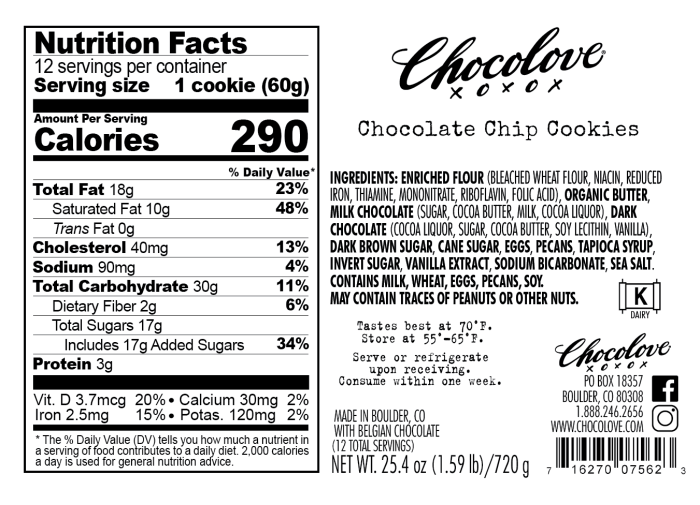
Chocolate chip cookie nutrition facts – Let’s dive into the calorie content of chocolate chip cookies, a crucial factor for anyone watching their intake. Understanding calorie counts per cookie and per serving, along with how serving sizes impact overall calorie consumption, is key to making informed choices. We’ll also briefly compare the calorie density of these delicious treats to other baked goods.
Calorie counts in chocolate chip cookies vary significantly depending on the recipe and brand. Factors like the type and amount of butter, sugar, and chocolate chips all play a role. Homemade cookies often have a higher calorie count than commercially produced ones, which might use leaner ingredients or portion control to meet specific nutritional targets.
Calorie Counts Per Cookie and Serving Size
The following table provides estimated calorie counts for different brands and homemade recipes. Keep in mind that these are averages and can fluctuate based on specific ingredients and preparation methods. Always refer to the nutrition label on the packaging for the most accurate information.
| Brand/Recipe | Calories per Cookie | Calories per Serving |
|---|---|---|
| Homemade (standard recipe) | 150-200 | 300-400 (2 cookies) |
| Brand A (store-bought) | 120-140 | 240-280 (2 cookies) |
| Brand B (store-bought, reduced fat) | 100-120 | 200-240 (2 cookies) |
Serving Size and Overall Calorie Intake
The relationship between serving size and overall calorie intake is directly proportional. A larger serving size inherently means a higher calorie consumption. For instance, consuming two cookies instead of one doubles the calorie intake. This is true regardless of whether the cookies are homemade or store-bought. Paying close attention to serving sizes, as indicated on packaging or in recipes, is vital for managing daily calorie intake.
Calorie Density Compared to Other Baked Goods
Chocolate chip cookies are relatively calorie-dense compared to some other baked goods. For example, a single chocolate chip cookie might contain a similar number of calories to a larger slice of angel food cake, which is significantly less dense. However, a muffin or brownie might contain a comparable or even higher calorie count per serving. The calorie density depends heavily on the ingredients and preparation methods of each baked good.
For instance, a dense, richly buttered brownie would have a higher calorie density than a lighter, less buttery muffin.
Impact of Ingredients on Health
Let’s delve into the nutritional landscape of chocolate chip cookies, examining the health implications of their key components. Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of these ingredients helps us make informed choices about our consumption. We’ll explore the effects of various ingredients on our bodies, focusing on sugar, fats, and other components.
Potential Health Benefits and Drawbacks of Ingredients
The ingredients in chocolate chip cookies offer a mixed bag of nutritional effects. Some provide benefits, while others present potential drawbacks. It’s crucial to consider the balance and moderation in consumption.
- Benefits:
- Fiber from oats (if included): Oats contribute soluble fiber, which can help lower cholesterol levels and promote healthy digestion. A cookie recipe incorporating rolled oats would increase the fiber content.
- Antioxidants from chocolate: Dark chocolate, often used in higher-quality cookies, is rich in flavonoids, powerful antioxidants that may help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. However, the amount of dark chocolate in a typical chocolate chip cookie is usually small.
- Drawbacks:
- Saturated fats from butter: Butter is high in saturated fat, which can raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease if consumed in excess. Many recipes rely heavily on butter for flavor and texture.
- Refined sugars: The high sugar content contributes to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, and tooth decay. The simple sugars are rapidly digested and lead to spikes in blood sugar.
- High calorie density: Chocolate chip cookies are calorie-dense, meaning they pack a lot of calories into a small serving size. Regular consumption can lead to weight gain if not balanced with overall dietary intake and exercise.
Impact of Sugar Content on Blood Sugar Levels and Overall Health
The high sugar content in chocolate chip cookies significantly impacts blood sugar levels. Refined sugars, such as sucrose and high-fructose corn syrup, are rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, causing a sharp rise in blood glucose. This sudden surge can lead to insulin resistance over time, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. For example, consuming several cookies can cause a significant spike in blood sugar, especially for individuals already predisposed to insulin resistance.
This rapid fluctuation in blood sugar levels can also lead to energy crashes and increased cravings for more sugary foods, creating a cycle of unhealthy eating habits.
Effects of Different Types of Fats on Cholesterol Levels
Chocolate chip cookies often contain a mix of saturated and unsaturated fats. Butter, a common ingredient, is primarily saturated fat. Saturated fats raise LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Conversely, unsaturated fats (found in some oils like vegetable oil, if used in a recipe) can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol, contributing to better heart health.
Chocolate chip cookies, oh the deliciousness, but let’s be real about the sugar rush. Understanding their nutritional profile is key, and it’s interesting to compare that to the sweetness of fruits. For instance, consider the simple, yet surprisingly complex, nutritional makeup of nutrition facts red grapes , a much healthier alternative. Then, returning to those cookies, we see the stark contrast in sugar content, highlighting the importance of mindful snacking.
The ratio of saturated to unsaturated fats in a cookie significantly impacts its effect on cholesterol. A cookie recipe relying heavily on butter will have a more negative impact on cholesterol levels compared to one using a higher proportion of unsaturated fats.
Dietary Considerations and Modifications
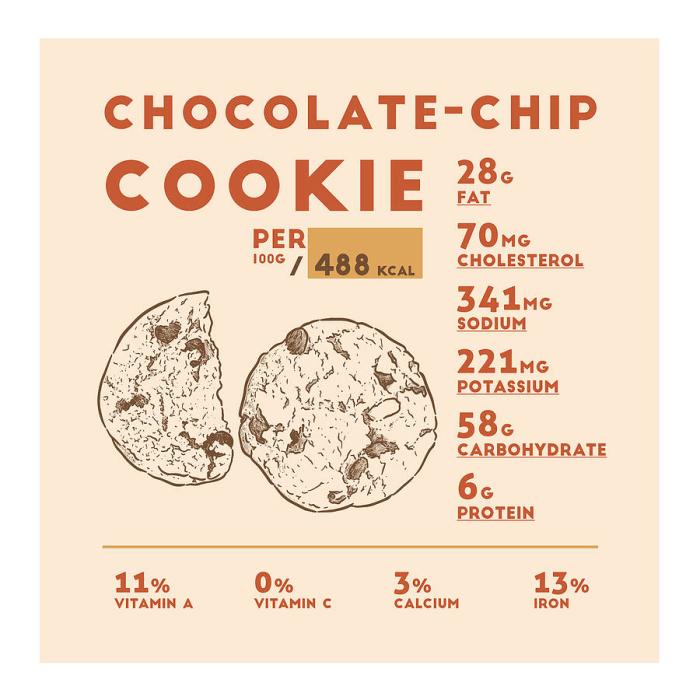
Chocolate chip cookies are a beloved treat, but their traditional recipe isn’t always suitable for everyone. Let’s explore how we can adapt this classic recipe to accommodate various dietary needs and preferences, focusing on maintaining deliciousness while improving nutritional profiles. We’ll look at gluten-free, vegan, and reduced-sugar variations.
Gluten-Free Chocolate Chip Cookies, Chocolate chip cookie nutrition facts
Making gluten-free chocolate chip cookies involves replacing the all-purpose flour with a gluten-free blend. This blend usually contains a mix of flours like almond flour, rice flour, tapioca starch, and sometimes xanthan gum to improve texture and binding. The nutritional impact will depend on the specific gluten-free blend used, but generally, you’ll see a decrease in carbohydrates and potentially an increase in fiber and protein, depending on the flour blend’s composition.
The calorie count might be slightly altered, but the overall impact on the taste should be minimal with a well-chosen blend.
| Ingredient | Original Recipe | Modified Recipe | Nutritional Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flour | All-purpose flour | Gluten-free flour blend (e.g., almond flour, rice flour, tapioca starch, xanthan gum) | Reduced carbohydrates, potentially increased fiber and protein depending on blend. |
| Other Ingredients | Butter, sugar, eggs, chocolate chips | Butter, sugar, eggs, chocolate chips (may need slight adjustments in quantity for optimal texture) | Minimal change, as the primary change is in the flour. |
Vegan Chocolate Chip Cookies
Creating vegan chocolate chip cookies requires replacing the butter and eggs. For butter, you can substitute vegan butter or coconut oil, which can slightly alter the flavor profile and texture. Flax eggs (ground flaxseed mixed with water) or applesauce can replace eggs, impacting moisture and binding. The nutritional profile will vary depending on the substitutes used; for example, coconut oil will add saturated fat.
The overall calorie count may not differ significantly, but the fat profile will change.
| Ingredient | Original Recipe | Modified Recipe | Nutritional Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Butter | Butter | Vegan butter or coconut oil | Change in fat profile; coconut oil increases saturated fat. |
| Eggs | Eggs | Flax eggs or applesauce | Change in binding and moisture content, potential reduction in cholesterol. |
| Other Ingredients | Sugar, flour, chocolate chips | Sugar, flour, chocolate chips | Minimal change. |
Reduced-Sugar Chocolate Chip Cookies
Lowering the sugar content in chocolate chip cookies can significantly impact their sweetness and texture. You can reduce the amount of granulated sugar by substituting with a sugar alternative like stevia, erythritol, or a sugar alcohol, or by simply using less sugar. This will reduce the calorie and carbohydrate content, impacting the overall sweetness and potentially the texture, requiring minor adjustments to other ingredients for optimal results.
The nutritional impact is a significant reduction in added sugar and calories.
| Ingredient | Original Recipe | Modified Recipe | Nutritional Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sugar | Granulated sugar | Reduced granulated sugar, or sugar substitute (e.g., stevia, erythritol) | Significant reduction in added sugar and calories. May affect sweetness and texture. |
| Other Ingredients | Butter, eggs, flour, chocolate chips | Butter, eggs, flour, chocolate chips (minor adjustments may be needed) | Minimal change except for the reduced sugar. |
Portion Control and Calorie Management
Portion control is crucial for managing calorie and nutrient intake from chocolate chip cookies. A standard serving size might be 2-3 cookies, depending on the size. Sticking to a predetermined number of cookies, rather than indulging freely, helps manage overall calorie consumption and nutrient balance within a daily diet. For example, if one cookie contains approximately 150 calories, consuming three cookies would result in a 450-calorie intake from cookies alone.
This should be factored into daily caloric goals.
Clarifying Questions
Are chocolate chip cookies a good source of fiber?
It depends on the recipe! Oats and some flours can add fiber, but generally, cookies aren’t a
-major* fiber source.
How much sugar is typically in a chocolate chip cookie?
That varies wildly depending on the recipe and brand, but it’s often surprisingly high. Check the nutrition label!
Can I make gluten-free chocolate chip cookies?
Absolutely! Many gluten-free flour blends work well as substitutes.
Are there any vitamins or minerals in chocolate chip cookies?
Small amounts of some vitamins and minerals can be found depending on the ingredients, but they’re not a significant nutritional source.
