Ingredients and their Nutritional Impact

Reese’s nutrition facts – Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups, a beloved confectionery treat, derive their characteristic flavor and texture from a blend of ingredients, each contributing to the overall nutritional profile. Understanding these ingredients and their impact is crucial for making informed choices about consumption. This section details the major components and their nutritional effects.
Understanding Reese’s nutrition facts requires considering the ingredients. The creamy peanut butter filling, for instance, contributes significantly to the overall fat and sugar content. For a comparison of high-quality protein sources, it’s helpful to examine the nutritional profile of other foods, such as the egg yolk nutrition facts , which offer a different balance of nutrients.
Returning to Reese’s, mindful consumption is key to balancing enjoyment with nutritional awareness.
The primary ingredients are milk chocolate, peanut butter, sugar, and various emulsifiers and stabilizers. These components interact to create the distinctive taste and texture, but their individual nutritional contributions vary significantly.
Major Ingredients and Nutritional Contributions
The following table summarizes the major ingredients in Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups and their respective nutritional contributions. It’s important to note that the exact nutritional values can vary slightly depending on the size of the cup and the specific manufacturing batch.
| Ingredient | Nutritional Contribution | Type of Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk Chocolate | Provides carbohydrates (primarily sugars), fat (saturated and unsaturated), and some protein. A significant source of calories. | Energy, flavor, texture | The cocoa butter in chocolate contributes to its smooth texture and rich flavor, while the sugar provides sweetness and energy. |
| Peanut Butter | Offers protein, healthy fats (unsaturated), fiber, and some vitamins and minerals. A good source of energy. | Protein, healthy fats, fiber | Peanuts are a source of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are considered healthier than saturated fats. The protein contributes to satiety. |
| Sugar | Provides quick energy but lacks essential nutrients. Excessive consumption can contribute to weight gain and other health issues. | Energy, sweetness | Sugar is a simple carbohydrate that is rapidly digested and absorbed, leading to a quick energy boost, but also a potential blood sugar spike. |
| Emulsifiers & Stabilizers | These ingredients help maintain the texture and shelf life of the product but generally have minimal nutritional value. | Texture, shelf life | Lecithin, a common emulsifier, helps blend the chocolate and peanut butter, creating a smooth, consistent product. |
Role of Different Types of Fats
The fat content in Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups comprises both saturated and unsaturated fats. Understanding the difference is important for assessing their impact on health. Saturated fats, primarily from the milk chocolate, are associated with raising LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels when consumed in excess. Unsaturated fats, predominantly from the peanut butter, are generally considered healthier and can help lower LDL cholesterol and raise HDL (“good”) cholesterol levels.
The overall balance of these fats contributes to the product’s nutritional profile and potential impact on cardiovascular health. Moderation in consumption is key to minimizing potential negative effects from the saturated fat content.
Nutritional Considerations and Health Implications
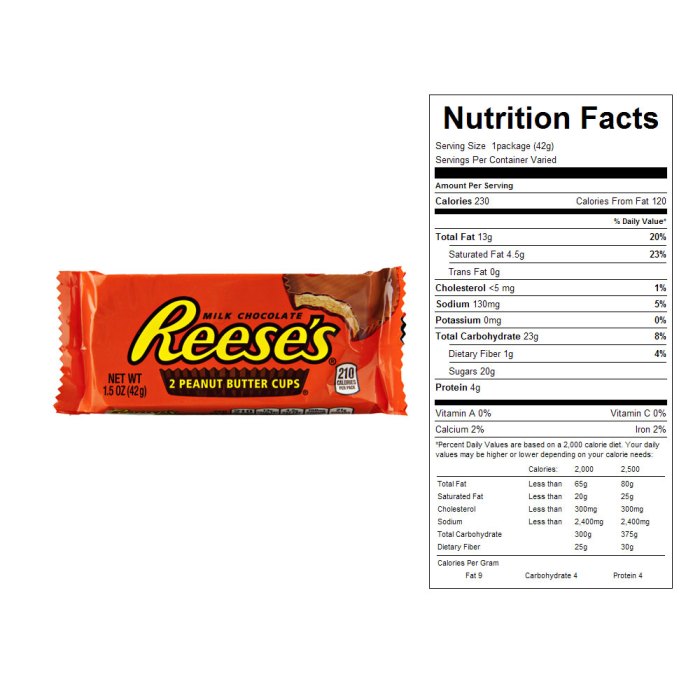
Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups, while undeniably delicious, present a significant nutritional challenge due to their high sugar and fat content. Regular consumption can contribute to various health concerns if not carefully managed. Understanding the potential impact on weight management and overall well-being is crucial for making informed choices.Regular consumption of Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups, with their high sugar and saturated fat content, can have several implications for various bodily systems.
The high sugar content contributes to increased blood glucose levels, potentially leading to insulin resistance and, over time, an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. The high saturated fat contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. Furthermore, the high caloric density contributes to weight gain if intake exceeds energy expenditure, potentially leading to obesity and related health problems.
Impact of High Sugar and Fat Intake on Health
High sugar intake leads to a spike in blood glucose levels, forcing the pancreas to release more insulin. Chronic high blood sugar damages blood vessels, leading to complications in the eyes (retinopathy), kidneys (nephropathy), and nerves (neuropathy), common in diabetes. Additionally, excess sugar can contribute to inflammation throughout the body, potentially increasing the risk of chronic diseases. High fat intake, especially saturated and trans fats, raises LDL (“bad”) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis (plaque buildup in arteries), which can lead to heart attacks and strokes.
The liver also plays a crucial role; excess sugar and fat can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), potentially progressing to cirrhosis. Weight gain resulting from excess calorie intake can further strain the heart, joints, and respiratory system. Imagine a scenario where an individual consumes several Reese’s cups daily; the cumulative effect over time can significantly increase their risk for these conditions.
For example, a study published in the “American Journal of Clinical Nutrition” showed a direct correlation between high sugar consumption and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Similarly, numerous studies link saturated fat intake to elevated cholesterol and cardiovascular disease.
Recommendations for Mindful Consumption, Reese’s nutrition facts
It’s important to acknowledge that Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups can be enjoyed occasionally as part of a balanced diet. However, mindful consumption is key for individuals concerned about their health. Moderation is paramount. Limiting intake to one or two small pieces per week, rather than daily consumption, can significantly reduce the risk of negative health consequences. Paying attention to portion sizes and choosing healthier alternatives some of the time can also contribute to a balanced dietary approach.
Consider pairing the treat with a more nutrient-rich snack, like a piece of fruit, to help balance the nutritional profile. Finally, regular physical activity helps burn calories and manage weight, mitigating some of the negative effects of high sugar and fat intake. This holistic approach to health management ensures that occasional indulgence doesn’t derail overall well-being.
FAQ Insights: Reese’s Nutrition Facts
Are Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups gluten-free?
Yes, Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups are generally considered gluten-free, but always check the ingredient list for potential cross-contamination.
How much sugar is in a mini Reese’s Peanut Butter Cup?
The sugar content varies slightly depending on the specific mini-cup size and production batch. Check the nutritional information on the packaging for the most accurate data.
Are there any Reese’s products with lower sugar content?
Hershey’s, the parent company, does not currently offer a significantly lower-sugar version of Reese’s Peanut Butter Cups. However, portion control is key to minimizing sugar intake.
What are the long-term health effects of eating too many Reese’s?
Regular consumption of high-sugar, high-fat foods like Reese’s can contribute to weight gain, increased risk of type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other health problems. Moderation is key.
